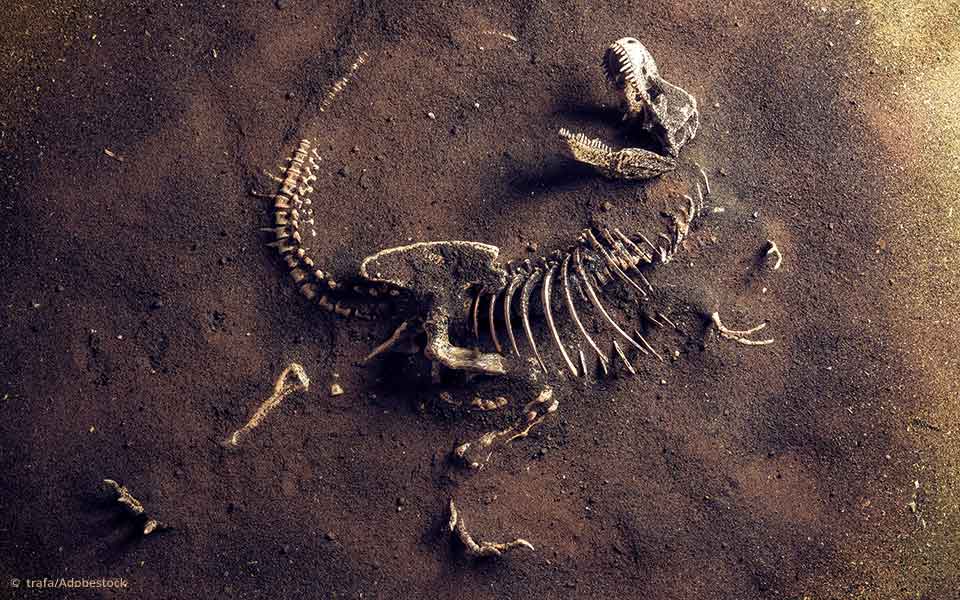

Fossilization is rare, as normally when an organism dies, its organic material gets completely decomposed, leaving only the hard skeleton behind. Fossils are formed under exceptional circumstances, which are still not well understood, in which organic material or “soft tissue” is preserved due to quick burial and isolation shortly after death. After millions of years, fossils are excavated by paleontologists, studying their morphological and microscopic features to gain valuable biological and evolutionary insights. In dinosaurs, soft tissue preservation has been reported since the 1960s, and mostly the bones have been studied.
How to detect organic compounds in fossils
Remarkably, bone histology is preserved in dinosaur fossils, even those aged more than 200 million years, and microstructures such as osteocytes and blood vessels were detected. The microstructures often resemble those of the fossil’s living relatives. To confirm this, analytical chemists use advanced sensitive instruments to detect organic compounds in fossils, part of an evolving field known as molecular paleontology. Typically, destructive techniques, like mass spectrometry, which destroy the sample, and non-destructive techniques, like Raman spectroscopy, after which the sample is recovered, are employed. One important factor to remember is that some molecules are more robust than others by nature. Among the molecules with high preservation potential are fats, but it is unlikely to find DNA, so Jurassic Park fans will be disappointed to know that cloning dinosaur DNA isn’t possible. Since the 1990s, several dinosaur specimens have been reported to contain preserved organic compounds in their bones, mainly proteins and pigments. Trabecular bone extracts of the 66 million-year-old Tyrannosaurus rex has been found to contain traces of heme, the blood pigment, while peptides of collagen have been detected in the bones of T. rex and an 80-million-year old Brachylophosaurus canadensis.
Revealing Secrets and facing Challenges
This exciting field continues to reveal new secrets, but there are challenges, especially in ruling out contamination to confirm that the organic compound indeed belongs to the fossil. One thing’s for sure: Your next visit to a natural history museum will not be the same again due to your altered perception of how these impressive fossils were formed!
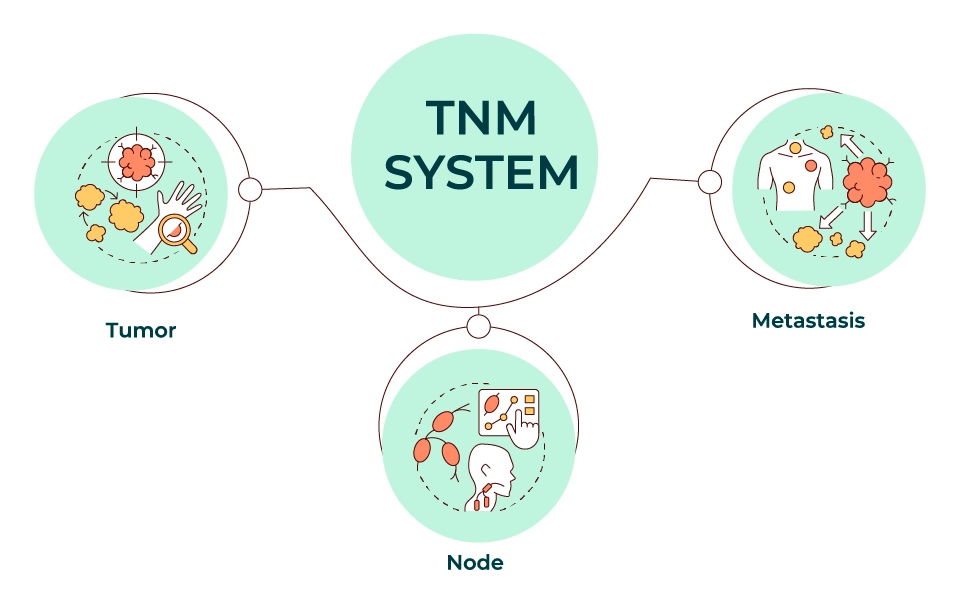
Wie funktioniert die Stadieneinteilung bei Krebs?
Heute ist für die Stadieneinteilung das sogenannte TNM-System maßgeblich. Es arbeitet mit den drei Kategorien „Primärtumor“ (englisch: „Tumor“), „Lymphknotenbefall“ („Node“) und „Metastasierung“ („Metastasis“). Die Stadieneinteilung bei Krebs war zunächst ein...

What Non-Nuclear Substance Is the Most Explosive?
Answering this questions leads us to the special competition: “Octanitrocubane (ONC) vs. the Rest”. It raises another question: How Do the Most Explosive Molecules Stack Up? In the world of energetic materials, few names spark as much curiosity—and awe—as...

What Is the Most Expensive Substance on Earth?
Antimatter When you ask people what the most expensive substance on Earth is, you get all kinds of answers: they name diamonds, gold, plutonium, saffron – even printer ink may be a candidate. But the real answer? It’s not in your jewelry box or your kitchen spice...

Wiley-VCH – 100 Years of Growing Knowledge
We have reason to celebrate: It’s our 100th year that we are publishing for the scientific community, for students, instructors, practitioners and researchers all over the world. From academic and professional learning up to the latest professional standards and...

